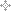Argon-1 Computer
Home → Articles → Argon Family of Computers → Argon-1 Computer
A. A. Pereshivkin
- Argon-1 was a vehicle-based computer
- The development team chiefs: S. P. Solovyov, S. N. Tsaplin, A. A. Pereshivkin. The development team: L. I. Bochkarev, M. Sh. Bugov, V. A. Grinkevich, N. N. Efimov, N. A. Zykov, Yu. N. Maksakov, G. P. Stupakova, V. M. Ternovsky, A. Ya. Tyurin.

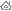
Argon-1 Computer
- Development organization: the Scientific Research Institute of Electronic Machines (NIIEM).
- Manufacturers: Astrakhan machine-building plant "Progress", Frunze computer plant (under the Ministry of Radio Industry of the USSR).
- The development was completed in 1969.
- Commercial production began in 1971.
- Argon-1 became out of production in 1980.
- Applications: forces automated control systems.
- More than 2000 were manufactured during the production period.
- The system architecture: single-address computer with parallel processing, structurally close to a general purpose computer. Computer included an exchange and calculations device, control console, light indicator and power supply unit. Input/output was carried out automatically through an I/O device or manually by operator's commands. It was possible to add memory units.
It used fixed point number type with 24 bit word length.
Its instruction set included 30 instructions and its execution times were respectively: addition - 16 ms, multiplication - 128 ms, division - 224 ms.
There was one index register.
RAM capacity was 512 words (expanded up to 1,024 words), ROM capacity for programs and constants was 2х4,096 words (expanded up to 4 х 4,096 words) and ROM capacity for changeable constants was 64 words.
Interrupt channels - 4, input interval - code converters - 2, output code - interval converters - 2, single commands channels - 18.
Digital exchange bus had 28 digital and 5 control bits and test, program and hardware checking (by mod 3).
- Components: hybrid ICs Tropa-1 and special modules.
- Construction: the computer was constructed as a computing device and an exchange device units combined mechanically and electrically into a mono-block structure, and several other separate units such as: control console, light indicator and power supply connected by cables. The printed circuit boards in all units were assembled in a book-like package and interconnected by a rubber back with flexible wires.
- Technology: unified double-sided printed circuit boards.
- Software: application programs, a standard programs set, test programs.
- Specifications:
- Opetrating temperatures - from -40 to 50°С.
- Humidity - up to 98% at 35°С.
- Atmospheric pressure - up to 200 mm Hg.
- Vibration - up to 5 g (from 1 to 300 Hz).
- Shock - up to 15 g (from 5 to 10 ms).
- Volume - 211 q. dm.
- Weight - 92 kg.
- Power consumption - 350 W.
- MTBF - 150 h.
- Features: the first vehicle-based computer for military automated control systems; used as a base model in 70 defense objects.